Those who work in the trade may know that the common logistics for cross-border trade include container freight, air freight (including air courier and air cargo) and land freight.
But if you are going through international trade, you are new to it. Don’t worry, and we have made some infographics with our full experience. And you need to take some time to look at each kind of exact logistics working flow. Air freight and sea freight are more frequently used in international shipping, and which one is better for your business?
Part 1. Sea Freight (LCL and FCL Shipping)
I believe that buyers or importers have more or less experience of shipping the goods from China via sea freight. But if you may not know how the goods were shipped. Today we share the key points in maritime transport so that you can be easy to learn how sea freight works.
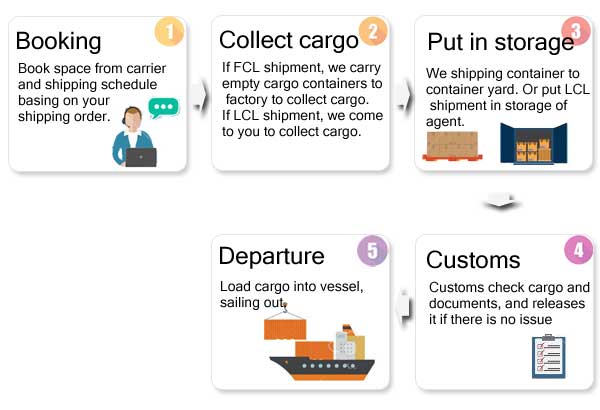
Inquiry shipping schedules and prices: estimate costs to determine the shipment schedule when the goods are ready.
Booking space: booking space based on how many cargoes, LCL or FCL?
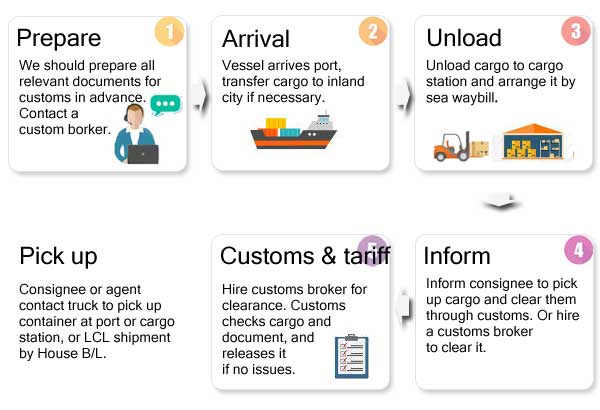
Transporting container into the loading port, customs clearance, the provision of declaration documents, confirmation of B/L.
After the goods arrive at the destination port, get the Pickup bill of lading (B/L) synchronized logistics status to buyers.
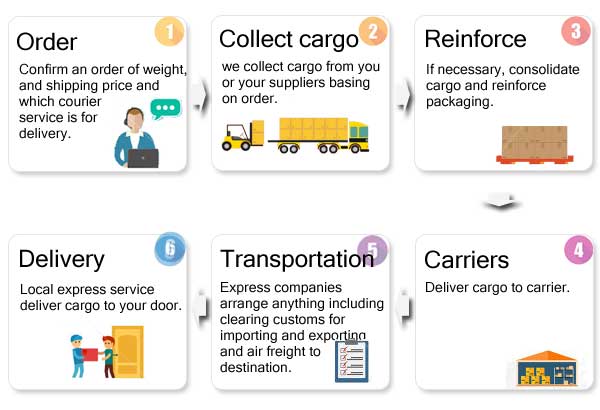
Part 2. Air Freight (Air Cargo and Courier Service)
To receive them in time, you are trying to buy some samples or dozens of kg of goods in the Chinese market. While controlling costs, it is a choice to choose an air courier if shippers need a door-to-door delivery.
If you have a large cargo (such as 200 kg of goods) that needs to be sent from your supplier as soon as possible, you should choose air cargo service as the first option.
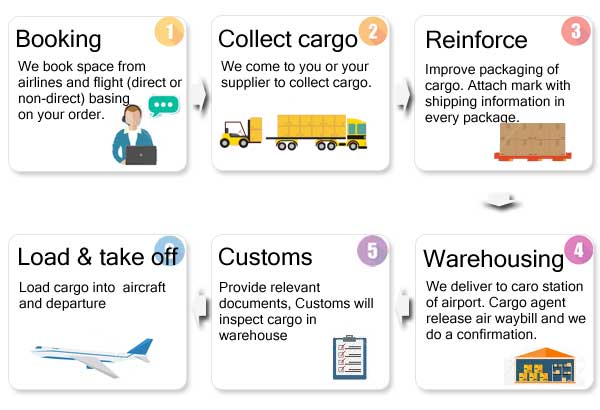
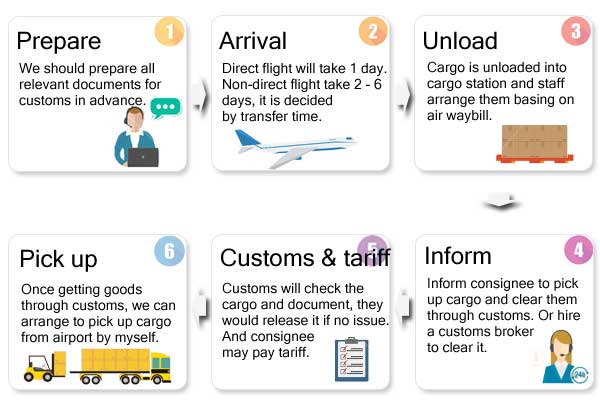
Door-to-door Service Fulfilled by Express Company(DHL, FedEx, UPS, TNT)